Rules for safe behavior during a thunderstorm. Presentation on the topic "safety measures during a thunderstorm" Presentation on the topic rules of behavior during a thunderstorm
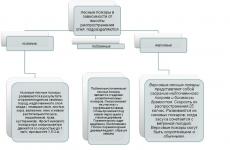
If you are in a rural area: close windows, doors, chimneys and vents. Do not light the stove because the high temperature gases coming out of the stove pipe have low resistance. Don't talk on the phone: lightning sometimes strikes wires stretched between poles.
During lightning strikes, do not come close to electrical wiring, lightning rods, roof gutters, antennas, do not stand near a window, and if possible, turn off the TV, radio and other electrical appliances.
If you are in the forest, then take cover in a low-growing area of the forest. Avoid shelter near tall trees, especially pine, oak and poplar trees.
Do not be in a body of water or on its shore. Move away from the shore, go down from a high place to a low place.
In the steppe, field, or in the absence of shelter (buildings), do not lie on the ground, exposing your entire body to electric current, but squat down in a hollow, ravine or other natural depression, clasping your legs with your hands.
If a thunderstorm hits you while playing sports, stop immediately. Place metal objects (motorcycle, bicycle, ice ax, etc.) to the side, move away from them 20-30 m.
If a thunderstorm finds you in your car, do not leave it, while closing the windows and lowering the radio antenna

Forest fires

Fire safety rules in forests
Do not light fires in young coniferous forests; in places with dry grass; under the forest canopy; on old fire pits; in forest areas subjected to windfall and windfall; on peat soils; on cutting areas that have not been cleared of logging residues and harvested wood.
If necessary, you can make a fire in open places, surrounding it with a mineralized strip of at least 0.5 m. When necessary, the fire should be filled with water or covered with earth.
Do not throw away burning matches, cigarette butts or ash from smoking pipes.
Do not fill the tanks of internal combustion engines with fuel while the engines are running.
Do not operate machines with a faulty power supply system.
Do not smoke or use open flames near vehicles being refueled.
Do not burn dry grass in forest clearings and meadows, stubble in fields and land adjacent to forests
in protective and landscaping forest plantations.

If you find yourself near a fire in a forest or on a peat bog and you do not have the ability to localize it, prevent the spread and extinguish the fire on your own, immediately warn all people nearby about the need to leave the danger zone.
Organize their exit onto a road or clearing, a wide clearing, to the bank of a river or reservoir, or into a field.
Leave the danger zone quickly, perpendicular to the direction of fire movement.
If it is impossible to escape the fire, enter a body of water or cover yourself with wet clothes.
When you go out into an open space or clearing, breathe the air near the ground - there it is less smoky, while covering your mouth and nose cotton-gauze bandage or rag.
If you find yourself near a fire in a forest or peat bog
After leaving the fire zone, report the location, size and nature of the fire to the local administration, forestry or fire service, as well as the local population.
The flames of small ground fires can be knocked down by overwhelming them with branches of deciduous trees, filling them with water, throwing them with wet soil, or trampling them underfoot.
Peat fires are extinguished by digging up burning peat and pouring water on it.
When extinguishing a fire, act carefully, do not go far from roads and clearings, do not lose sight of other participants, maintain visual and audio contact with them.
When extinguishing a peat fire, keep in mind that deep craters can form in the combustion zone, so you should move carefully, having first checked the depth of the burnt layer.

Classification of man-made emergencies
Transport accidents |
|
Hydrodynamic |
and disasters |
Fires, explosions, |
|
bomb threats |
Accidents at wastewater treatment plants |
Blowout accidents |
|
(threat of release) |
||
structures |
||
Chemically hazardous substances |
||
Man-made emergency |
Blowout accidents |
|||
Accidents in utilities |
(threat of release) |
||
life support systems |
radioactive substances |
||
Electrical accidents |
Blowout accidents |
||
(threat of release) |
|||
energy |
|||
biologically hazardous |
|||
systems |
Sudden collapse |
||
buildings, structures |
|||

Explosion and fire hazardous
Explosion and fire hazardous facilities are those facilities where flammable products or products that acquire the ability to ignite and (or) explode under certain conditions are produced, stored, transported.
Accidents that occur at explosion- and fire-hazardous facilities are characterized by explosions and fires and pose a particular danger to the population.
“Objects of living and inanimate nature” - What happened to the plant. Didactic material. Its tail wags under the bridge. Seasonal phenomena. Read the text. Nature. Definition of natural phenomena. Introduction to the topic. Living and inanimate nature. Crossword "Living - nonliving." Learning new things.
“Nature of the native land” - To recognize animals, insects, birds. So that we can admire plants and animals. Why do children need to study the nature of their native land? Because plants purify the air. To know the inhabitants of the forest. Do not get poisoned by poisonous mushrooms or berries. To know and study our region, to know more about our region.
“Nature corner” - Lesson summary. Begonia Chlorophytum. What flowers? What is a corner of nature? Practical work. What is the fish's body covered with? Veiltail. Hamster Parrot. Guinea Pig Rabbits. What leaves? Swordtail Guppies. How can you grow a houseplant? Consider the plant. Let's draw a conclusion. Indoor flowers. Our corner of nature.
"Nature" - The goal of the project. A group of theorists. Nasturtium. Dandelion. What do we want to know? Chamomile. Fundamental question. A group of sociologists. Viola. Is it necessary to protect nature? - this question is not difficult to answer. Outputs (results) of student activities. Data. Group of practitioners. What flowers would you like to see in the flower beds of your home?
“Living and inanimate nature” - Tulip. Objects of nature do not include only those things made by human hands. Live nature. Nature can be: living, non-living. Water, Inanimate nature. Non-living. The Earth is the chosen one of the solar system on which life exists. Human. Water. “Saving nature means saving life!” Alive. Squirrel, Ant,
“Inanimate and living nature” - Sky... Journey of a droplet. Sun... Inanimate nature in autumn. The first drop fell - drop! You can't live without water. Well, look at the shoes - they became wet. Air... Insects... Exercise. Inanimate nature in spring. Inanimate nature in winter. Every living thing needs clean water. Let's run away from the rain and sit under a bush. Water must be conserved.
There are a total of 36 presentations in the topic
1 slide

2 slide
Purpose of the study: To understand the essence of the observed natural phenomenon; Explain a physical phenomenon based on physical laws and theories; Discuss rules of behavior during a thunderstorm.

3 slide
A thunderstorm is a beautiful but dangerous natural phenomenon. In ancient times, people could not explain why thunderstorms occur. They believed that the gods were angry with people. In ancient times, the Eastern Slavs revered the god Perun, the “creator” of lightning and thunder. Later, our ancestors attributed thunder and lightning to the “activities” of Elijah the prophet, who “rides across the sky in a thundering chariot and in anger throws stones and fiery arrows to the ground.”

4 slide
Now people know that thunderstorms occur because the air in one place is very hot, and in another, on the contrary, it is very cold. Where moist and warm air met dry and cold air, a thundercloud formed. Electrical discharges - lightning - always appear in a thundercloud.

5 slide
Thanks to the hard work of researchers, it was possible to show that there is nothing supernatural in the phenomenon of thunder and lightning, that there is no place for divine activity in it and there is no reason for superstitious fears. Among the first scientists to prove the electrical nature of thunderstorms were the great Russian scientist M.V. Lomonosov and his friend G.V. Richman. During experiments in 1753, Richmann was killed by ball lightning. Richman G.V. Lomonosov M.V.

6 slide
A thunderstorm is an atmospheric phenomenon in which electrical discharges - lightning - accompanied by thunder occur inside clouds or between a cloud and the earth's surface. Typically, thunderstorms form in powerful cumulonimbus clouds and are associated with heavy rain, hail and strong winds.

7 slide
Lightning is a huge electrical spark or discharge in the atmosphere. Most often we observe lightning that resembles a winding river with tributaries. Such lightning is called linear; when discharged between clouds, their length reaches more than 20 km. An electrical discharge in the atmosphere in the form of linear lightning is an electric current. Approximately 65% of all lightning strikes have a maximum current of 10,000 A, but in rare cases it reaches 230,000 A. The time for the maximum current to flow in a lightning discharge is very short - about 100 microseconds.

8 slide
The lightning channel through which the current flows becomes very hot and shines brightly. The temperature of the channel reaches tens of thousands of degrees, and the air pressure rises to several hundred megapascals. Then the air expands, causing an explosion of hot gases. This is what we perceive as thunder. A lightning strike to a ground object can cause a fire.

Slide 9
Air conducts electricity differently in different places, so the electrical discharge travels to those places where the least resistance is encountered. This is why we often see a sinuous line of lightning. Lightning more often strikes tall structures, i.e. places where the thickness of the air layer between a thundercloud and a ground object is less - a tall building, a tall tree, etc. Lightning can strike a flat surface of the earth, but where the electrical resistance of the soil is less. For this reason, lightning strikes the banks of rivers and streams.

10 slide
Lightning can also produce magnetic effects: magnetize iron and steel objects, remagnetize a compass. It happened that this circumstance caused a change in the ship's course. Such “jokes” of lightning sometimes led to ship accidents.

11 slide
In cities, lightning is not dangerous; all tall buildings and structures have lightning rods. To protect yourself from a thunderstorm, a lightning rod is used. Rising along the lightning rod, positive charges neutralize negative ones. Very often this is enough for lightning not to strike at all. If lightning does strike, it it hits the lightning rod as if it were the tallest object. And it goes down the wires into the ground.

12 slide
If lightning strikes a person or animal, in most cases the strike is fatal. Therefore, when you are outside your home and see a thunderstorm approaching, you must leave dangerous places: mountains and hilltops, open peaks, banks of reservoirs. Do not approach tall single objects (pillars, trees). It is recommended to take shelter in a small depression on the hillside, choosing a place between two trees growing at a distance of 15 - 25 m. An unconscious lightning victim must be given artificial respiration until a doctor arrives.

Slide 13
Both the structure of the root and the tree's resistance to current play a role in lightning damage to trees. Trees with roots penetrating into deep aquifers of the soil are better “grounded”, so significant charges flowing from the ground accumulate on them, having a sign opposite to the sign of the charge of the clouds. For example, an oak tree has roots deep into the soil, so it is more often struck by lightning than others.
- The work was completed by a 4th grade student
- Evsikova Ekaterina
- Head: Mamontova L.V.
- A thunderstorm is a beautiful and majestic natural phenomenon. But a thunderstorm also carries a huge danger - lightning strikes. To protect yourself from them, you need to follow some rules.
- Science cannot fully understand the nature of lightning. Every year there are new surprises. Even installing a lightning rod does not guarantee complete protection of the building from troubles. A lightning rod protects against direct lightning strikes, but does not protect against so-called secondary effects. The fact is that when lightning strikes the ground or some object within a radius of up to 1500 meters from the building, there is a possibility of electrical discharges moving to it through various communications capable of conducting current: power supply systems, communications, gas pipelines. This causes a sharp increase in voltage in electrical networks, leading to various emergency situations - from burnout of microcircuits in household appliances to complete failure of electrical equipment. Specialists from the Ministry of Emergency Situations recommend turning off all household electrical appliances in the house during a thunderstorm and not using a regular telephone, not standing near windows and doors, and not touching water taps. This way you will protect both your equipment and your health from unexpected problems. Make sure there is no draft in the room, which could attract ball lightning. It is better not to light a stove or fireplace at this time, since the smoke coming out of the chimney has high electrical conductivity, and the likelihood of a lightning strike into the chimney increases.
- You cannot hide under tall trees, especially free-standing ones.
- When on the street, in a park area or in a forest, you should not hide under tall trees; it is better to move 30-40 meters away from them. The likelihood of lightning striking a particular tree is directly proportional to its height. Especially, as people say, poplars, oaks, pines and spruces “attract lightning.” Birches, maples, and hazel trees are practically not subject to lightning strikes. The danger increases if there are already trees nearby that have been previously struck by lightning. In the city, try to find shelter in a store or residential building as soon as possible; they have reliable lightning protection, unlike public transport stops. If there are no such options, you need to wait out the thunderstorm by squatting under low plants. It is better to turn off your cell phone when you are outside.
- Oddly enough, experts advise not to open your umbrella over yourself! Probably due to the presence of many metal parts on it. It is also quite dangerous to stand near a wall near which a tall tree grows; it is better to stay away from electrical wires, antennas and simply damp walls. It is not recommended to stay at high places and in open, unprotected places. Especially if there are metal or mesh fences, power lines, or large metal structures nearby.
- You cannot swim during a thunderstorm.
- When a thunderstorm approaches, those who like swimming and fishing are advised not only to immediately stop these activities, but also to move away from the reservoir. Don’t even think about looking for shelter in the floodplain bushes! If there is an open field around, you need to get to the nearest forest (but not a bunch of trees in an open area) or to a village as soon as possible (but do not run if a thunderstorm has already begun). At the same time, try to avoid, about two hundred meters away, isolated trees and other tall objects.
- But the car is a safe haven and it is better not to leave it during a thunderstorm. You need to close the windows and lower the car antenna, stop driving and wait out the bad weather on the side of the road or in the parking lot, located away from tall trees. Bicycles and motorcycles, on the contrary, are potentially dangerous at this time. They should be left away, laid on the ground and kept at least 30 meters away from them during a thunderstorm. It is even more dangerous to be in a tractor in an open field!
- End
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Rules of behavior for people when approaching and passing a thunderstorm front Prepared by primary school teacher T.I. Peremyshleva.
Formation of a thunderstorm front LIGHTNING is a spark discharge of an electrostatic charge of a cumulus cloud, accompanied by a blinding flash and a sharp sound (thunder).
Danger Lightning discharge is characterized by high currents, and its temperature reaches 300,000 degrees. A tree, when struck by lightning, splits and can even catch fire. Splitting of wood occurs due to an internal explosion due to the instantaneous evaporation of the internal moisture of the wood. A direct lightning strike for a person is usually fatal. About 3,000 people are killed by lightning around the world every year. Where does lightning strike? Static electricity discharge usually follows the path of least electrical resistance. Since the distance between the highest object, among similar ones, and the cumulus cloud is smaller, the electrical resistance is also smaller. Therefore, lightning will primarily strike a tall object (mast, tree, etc.).
Recommendations for the population during the passage of a thunderstorm front and basic rules for safe behavior during a thunderstorm. If you are in the house during the passage of a thunderstorm front, then: if possible, close windows, chimneys and ventilation openings; it is also not recommended to light stoves, because The smoke coming out of the chimney has high electrical conductivity and can attract an electrical discharge. For the same reason, during a thunderstorm, the fire should be extinguished. You should not be on the roof or near the down conductor or grounding conductor during a thunderstorm. During a thunderstorm, turn off the radio and television. Avoid using the telephone, including mobile phones. Do not use electrical appliances or touch metal objects. If your radio or television receiver has a personal antenna on the roof, it should be disconnected from the devices.
How to behave during a thunderstorm when you are at home If you are in the house when a thunderstorm front passes, then: if possible, close windows, chimneys and ventilation openings; it is also not recommended to light stoves, because The smoke coming out of the chimney has high electrical conductivity and can attract an electrical discharge. For the same reason, during a thunderstorm, the fire should be extinguished. You should not be on the roof or near the down conductor or grounding conductor during a thunderstorm. During a thunderstorm, turn off the radio and television. Avoid using the telephone, including mobile phones. Do not use electrical appliances or touch metal objects. If your radio or television receiver has a personal antenna on the roof, it should be disconnected from the devices.
If a thunderstorm finds you in an open area: turn off your mobile phone and other devices; it is also not recommended to use an umbrella; in the steppe, field, or in the absence of shelter (buildings), do not lie on the ground, exposing your entire body to electric current, but squat down in a hollow, ravine or other natural depression, clasping your legs with your hands.
If a thunderstorm catches you on the water Do not be in a body of water or on its shore. Move away from the shore, go down from a high place to a low place.
If a thunderstorm finds you in the forest, try to meet the thunderstorm in a clearing, do not look for protection under the crowns or separate trees, do not lean against their trunks, do not sit near the fire: a column of hot air is a good conductor of electricity, do not climb trees. Avoid shelter near tall trees, especially pine, oak and poplar trees.
If a thunderstorm finds you in the mountains, while on vacation in the mountains: immediately leave the danger zone, stop moving, avoid body contact with wet rocks, tight crevices, awnings and caves, if possible, isolate yourself from wet ground and rocks, using shoes with rubber soles, dry tent, sleeping bag, backpack, rope, tree trunk. Try to keep clothes, shoes, equipment, food, and medicines dry. Place metal objects at a distance of 15-20 meters from the location of people. In a tent: place the tent at a distance of at least 2 meters from the tree trunk and its branches, additionally secure the tent, cover it with waterproof film, place metal objects at a distance of 10-15 meters from the tent. Close all openings tightly, including the entrance, put on dry clothes and lie down. In a thunderstorm zone, you can weave a copper strip into the tent canopy and ground it using a metal rod driven into the ground.
Thunderstorm while driving a car If a thunderstorm finds you in your car, do not leave it, while closing the windows and lowering the radio antenna.
First aid for lightning strikes The main injuries from lightning strikes are: electrical trauma, paralysis, burns, loss of vision and hearing. Often these are accompanied by accompanying injuries: bruises, fractures, depression, stress. Despite short-term exposure to lightning, a person’s brain and heart can be paralyzed, and severe burns and death are common. There is a misconception that a person struck by lightning must be buried in the ground for a while. DO NOT DO THIS UNDER ANY CASE! Such actions worsen the condition of the victim and can hasten his death. Important!!! If there is a person next to you who is struck or shell-shocked by lightning, do not be afraid to touch him - there is no charge left in the victim’s body. We must remember that not every lightning strike is fatal! You can help a person by providing first aid: - quickly determine the condition of the victim - immediately carry out resuscitation measures: artificial respiration, chest compressions - warm the victim - treat burns and associated wounds - give analgin or solpadeine, give an anti-shock drug - urgently take the victim to a hospital institution.