The heat accumulator is an important element of the heating system of a comfortable and safe home. Heat accumulators for heating boilers Heating system for a private house with a storage tank
Companies involved in the development of engineering systems last years focus on the development of alternative technological solutions. Concepts and directions that do not involve the use of natural resources. At the very least, experts strive to minimize their consumption. A tangible benefit in this segment is demonstrated by a heat accumulator for a heating system, which is included in the existing engineering complex as an additional optimization component.
General information about heat accumulators
There are many modifications and varieties of heat accumulators, which are also called buffer heaters. The tasks that such installations perform are also different. As a rule, batteries are used to increase the efficiency of the main unit, for example a solid fuel boiler. In these cases, it is advisable to use such systems to carry out a monitoring function, which is difficult to implement in the process of servicing traditional boiler rooms in private homes. Most often, heat storage tanks with a capacity of up to 150 liters are used for this. In the industrial sector, of course, installations with a capacity of about 500 liters can also be used.
The tank itself contains elements that ensure maintenance of the required temperature of the medium. The very material from which the tank is made must be mated with layers of insulators. The active components are heating elements and copper pipes. The configuration of their placement in the tanks may differ, as well as the systems for controlling the operating parameters of the battery.
Operating principle

From the point of view of the drive, the main task is to ensure the ability to maintain the desired temperature regime, which is set by the user. As the boiler operates, the tank receives hot water and stores it until the heating system stops functioning. The conditions for maintaining temperature balance are determined by the insulating materials of the container and the internal heating elements. A classic heat accumulator for a heating system, in essence, resembles the operation of a boiler and is also integrated into the system. That is, on the one hand, the equipment is connected to a heat source, and on the other, it ensures the operation of direct heaters, which can be radiators. In addition, the system is often used as a full-fledged source of hot water for domestic needs in constant consumption mode.
Functions of thermal accumulators
As already noted, units of this type can perform different tasks, the requirements for which determine the criteria for choosing a particular system. The basic and main functions include the accumulation of heat from the generator and its subsequent release. In other words, the same tank collects, stores and transfers energy to the direct heating element. In combination with a solid fuel boiler, the system’s functions include protection against overheating. Automated and electronic control relays are ineffective in solid fuel units. Therefore, it is practiced to optimize the operation of the boiler using a heat accumulator, which naturally collects excess energy and returns it during temperature drops. Electric, gas and liquid generators are easier to control, but with the help of a battery they can be connected into a single complex and operated with minimal heat loss.
Where can a thermal accumulator be used?

It is advisable to use a heat storage system in cases where the existing heating unit does not allow sufficient control of its operation. For example, solid fuel boilers inevitably provide for maintenance moments when their capacities are not loaded. To compensate for heat loss, it makes sense to use such a system. Also, in the operation of water and electric heating systems, this solution is economically justified. A modern heat accumulator with automatic control can be configured to operate during certain periods of time when the most economical energy consumption tariff is in effect. So, for example, at night the system will conserve a certain volume which can be used for any needs during the next day.
Where is it undesirable to use heat accumulators?
The nature of the operation of buffer batteries is designed to ensure uniform heat transfer and smooth out surges during temperature changes. But this principle of operation is not always useful. For heating systems, which, on the contrary, require an accelerated increase or decrease in temperature, such an addition will be unnecessary. In such situations, increasing the potential of the coolant due to auxiliary ones will prevent rapid cooling and heating. In addition, it is worth noting that home heat accumulators for the most part make precise temperature control impossible. It would seem that such a solution could be optimal for heating systems operating in short intervals - it is enough to heat the container in advance and then use the ready energy at the appointed time. However, maintaining the optimal state of the coolant itself requires the consumption of a certain amount of energy. Therefore, for example, a boiler room used for irregular and short-term heating of a dryer can easily do without a battery. It’s a different matter if we are talking about a whole group of boilers that can be combined into one system using a buffer.
Battery characteristics

Among the main characteristics are the dimensional parameters of the unit, its capacity, maximum temperature and pressure indicator. For private homes, manufacturers offer small installations, the diameter of which can be 500-700 mm and the height - about 1500 mm. It is also important to consider weight, since in some cases specialists have to use concrete screeds to give the structure stability. The average heat accumulator weighs about 70 kg, although the exact value is directly related to the capacity and quality of the insulation of the tank. Performance characteristics come down to temperature and pressure. The first value is about 100 °C and the pressure level can reach 3 Bar.
Battery connection
A homeowner with knowledge in electrical engineering can not only independently connect a ready-made buffer to the heating system, but also completely assemble the structure. First you need to order a container in the form of a cylinder, which will become a working buffer. Next, in transit through the entire tank, it is necessary to conduct a return pipeline through the niche of the future heat accumulator. The connection should begin with the connection between the boiler return and the tank. From one component to the second, a place should be provided where the circulation pump will be installed. With its help, the hot coolant will move from the barrel to the shut-off valve and expansion tank.
You need to install the heat accumulator with your own hands in such a way that the most rational distribution of liquid throughout all rooms is assumed. To assess the quality of operation of the assembled system, you can provide it with thermometers and pressure sensors. Such equipment will allow you to evaluate how efficiently the battery will function through the connected circuits.
Water systems

A classic heat accumulator involves the use of water as an energy carrier. Another thing is that this resource can be used in different ways. For example, it is used to supply heated floors - the liquid passes through circulation pipes into a special coating. Water can also be used to ensure the operation of the shower and other needs, including technological, hygienic and sanitary purposes. It is worth noting that the interaction of boilers with water is quite common due to its low cost. Water heat accumulator is cheaper compared to electric heaters. On the other hand, they also have their drawbacks. As a rule, they come down to nuances in the organization of circulation networks. The greater the volume of resource consumed, the more expensive its organization is. Installation costs are one-time, but operation will be cheaper.
Solar systems
In water systems, the design includes a comb heat exchanger designed for a geothermal pump. But a solar collector can also be used. In essence, this creates a power plant center that optimizes the function of the heating plant by reserving energy from different sources. Although the battery solar heat less common, it can be used in standard heating systems. Solar collectors also retain energy potential, which is later spent on household needs. But it is important to consider that hot coolant in the form of water itself requires less energy than a solar battery. The best option The use of such batteries is the direct integration of panels into places where heating should be carried out without additional transformations.

How to choose heat?
It is worth starting from several parameters. To begin with, the functionality of the system and its performance indicators are determined. The tank must completely cover the volumes that are planned to be consumed during operation of the heating system. You shouldn’t skimp on control systems either. Modern relays With automatic regulators not only make programming of engineering systems convenient, but also provide protective properties. A properly equipped heat accumulator has protection against idle move and provides ample opportunities to indicate temperature conditions.
In the majority modern systems heating has an inherent flaw that makes it impossible effective organization heating using a periodic heating boiler. The problem lies not in the principle of fuel combustion, although not everything is smooth there either, but in the organization of heat transfer from a heat source - the combustion front of solid fuel into the air space of the living rooms of a house or apartment. Heat accumulators are designed to compensate for losses caused by periodic operation of the boiler. To be precise, a heat accumulator is necessary for any intermittent heating boiler.
The device, proudly called a heat accumulator for heating boilers, is a tank of significant capacity, reaching in some cases up to 10 tons of water, with a system of internal heat exchangers. What should the use of a heat accumulator provide:
- Safe accumulation of excess heat generated by the boiler into the coolant water flow;
- Increase the duration of the heating-cooling cycle of the boiler installation, thereby simplifying its maintenance, freeing it from the need to start it at night or at inconvenient times;
- Increase operating efficiency and increase the service life of heating boilers.
Interesting ! The primitive design of the heat accumulator for heating boilers allows you to make it yourself; you only need a water tank, pipes for connection, valve equipment and a welding machine.
In addition to a solid fuel heating boiler, systems also need to use a heat accumulator. electric boilers heating. In this case, the use of a heat accumulator is dictated artificial choice in favor of periodic heating, and only at night, when it is possible to use a more favorable preferential tariff.

The design of modern heating boilers is maximally optimized in terms of costs and production costs to please the manufacturer. A modern heating boiler is made of thin sheet steel with minimal expenditure on scarce and expensive copper and nickel, and operates as a “potbelly stove” stove.
There is not even a hint of a heat accumulator in its design. Such a heating boiler is, in principle, unable to accumulate thermal energy. Compare a modern pellet or coal boiler with the old heavy designs of cast iron heating boilers, or even better, with the design of an ordinary village stone stove. In the latter case, the functions of the heat accumulator are performed most efficiently brickwork, directly absorbing heat from the flame and evenly transferring it into the air of the room within 10-12 hours.
Therefore, a modern heating boiler is ineffective without a heat accumulator. A solid fuel unit will be indispensable in operation and will do without multi-ton heat accumulators if it has a system for automatically loading fuel into the firebox and subsequent cleaning of ash.
How does a heat accumulator work?
The purpose of the heat accumulator is to provide additional thermal energy to the water heating circuit after the heat generation by the heating boiler has decreased or stopped. To do this, there is a large amount of boiling water in a huge container at a pressure of about 3 atm. A heat exchanger is soldered into the tank body, through which heat is “pumped” into the battery and returned to the heating system. Often, an additional heat exchanger is built into the tank to produce hot water for the needs of the kitchen and bathroom.
The principle of mixing flows of different temperatures
To quickly warm up the room, the heat accumulator using three way valve switched off from the circuit of movement of the heated coolant. Only after the water flow in the pipes has warmed up above 60 o C is water from the heat accumulator reserve connected to the circuit. And while the boiler is running, heat goes in two directions: into the storage tank and into the heating radiators.
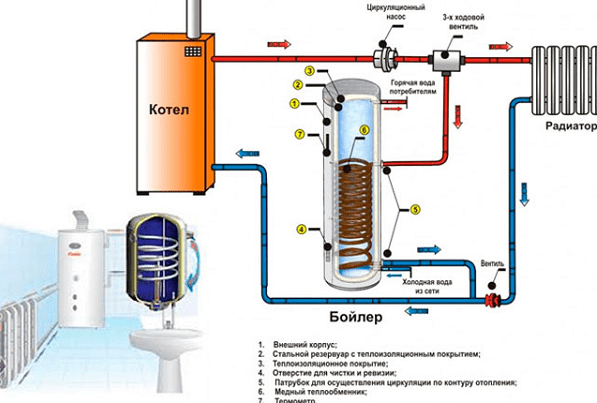
IN similar principle There are certain positive aspects:
- Rapid heating of the living space, and only after this the excess heat is discharged into the heat accumulator;
- The mixing principle provides efficient heat exchange;
- The water reserve in the heat accumulator is a strategic reserve for the boiler, thereby preventing its possible burnout if the water circulation in the heating plant is disrupted.
Important ! In such a scheme, any non-ferrous metals that produce an electrochemical couple with steel and aluminum should be excluded.
Ideally, the water circulating in the hot heat exchanger of the heating boiler should not mix with the coolant flowing throughout the heating system. Therefore, a different scheme is often used in heat accumulators - with hydraulic isolation and flow separation.
System with hydraulic isolation of thermal media
In this scheme, the heat accumulator plays the role of one of the elements of the heat supply circuit; it cannot be excluded from the flow. In fact, in the heat accumulator there is a constant transfer of heat from the dedicated “hot” circuit of the heating boiler and the rest of the water or coolant circulating in the heating system.
What does it give:
- The highly loaded heat exchanger of a heating boiler requires the use of special water purified from impurities and air oxygen. Only such water guarantees long term service of heat exchanger tubes and seals. The supply of the required amount of prepared water is stored in an additional boiler.
- By means of a special circuit of heated water from the heat accumulator tank, the temperature of the selected liquid can be easily adjusted, which simplifies the heating control system.
The disadvantages include the need for additional devices - two pumps: coolant circulation and power supply systems. Sometimes a couple of devices are used for backup - a voltage converter and an electric battery for a heating boiler. Otherwise, a power outage may lead to a serious accident in the primary circuit.
A more complex and improved scheme involves the use of two independent heat exchangers combined in one heat accumulator housing. This is a more rational way to organize the operation of a heat accumulator with high degree reservations. This is what we can recommend for those who want to make a heat accumulator for a heating boiler with their own hands.

Building a heat accumulator on your own
To manufacture a heat storage device, you need to determine the thermal power of the battery. There is a certain methodology for constructing an accumulating system. The amount of water in the battery is taken based on 30-40 liters of liquid for every 1000 W of boiler thermal power. In this case, for a house with 100 m2 of heated area, a capacity of 350-400 liters will be required. The best option will use a ready-made boiler tank, with sensors for water level, pressure and temperature.
If a system with admixture is chosen as the working scheme, which works properly even in the absence of special pumps, a three-position block valve will have to be additionally installed in the heating circuit.

Simpler schemes will require one or two heat exchangers to be installed in the tank
Important ! The Internet often recommends installing copper heat exchangers made of twisted copper pipe 15-17m long and with a “clearance” diameter of 15-20mm. The recommendation has dubious prospects, since copper and iron are in contact with hot water intensively corrode.

It is better to use a heat exchanger made of the same material as the container. This guarantees normal quality of the weld when installing the heat exchanger. In addition, in the cavity of the heat accumulator it is better to use anodic protection with magnesium electrodes, similar to that for electric hot water boilers. The outer walls of the heat storage tank are sheathed thermal insulation mats or mineral wool.
Promising options for heat accumulators
One of interesting solutions Small-sized batteries have become available, using low-melting paraffins or silicone oils instead of water. Thanks to the significantly higher heat capacity, it has become possible to use safe, small-sized storage systems for electric boilers in apartment heating systems. Instead of a 300-liter heavy tank, it is planned to use a two-section battery with a total volume of 50 liters of coolant, having a thermal reserve of 15 kWh.
For your information ! Most often, heat accumulators are used as a backup heat source when growing vegetables in greenhouses, to quickly heat the room during a sudden cold snap or frost.
When using a gas boiler, we do not need to independently maintain a certain temperature in the heating circuit - this is done automatically. But everything changes when a solid fuel boiler is installed in the house. The fuel in it burns unevenly, which leads to cooling or overheating of the heating system. A heat accumulator for heating will help compensate for these fluctuations and stabilize the temperature in the circuit. A capacious storage tank will be able to retain excess thermal energy, gradually releasing it into the heating system.
In this review we will look at:
- How heat accumulators for heating systems work;
- How to calculate the required volume of a battery tank;
- How storage tanks are connected;
- The most popular models of thermal storage devices.
Let's go through these points in more detail.
Operating principle of heat accumulators
If you install a solid fuel boiler in your house, there will be a severe need to regularly add more and more firewood. It's all about the limited volume of the combustion chamber - it cannot accommodate an unlimited number of logs. And their systems automatic feeding have not yet been invented, if you do not take into account pellet boilers with automation. In other words, you will have to monitor the operation of the heating system yourself.
These boilers develop maximum power at the moment when firewood is happily blazing in them. At this moment, they provide a lot of excess energy, so users dose the firewood carefully, placing it one log at a time. Otherwise the house will be too hot. There is nothing good about this, since this increases the number of approaches, which is already high. The problem is solved using a heat accumulator.
A heat accumulator for heating is a storage tank in which hot coolant accumulates. Moreover, energy is supplied to the heating circuit in a strictly dosed manner, which ensures temperature stability. Due to this, household members get rid of temperature fluctuations and frequent trips to lay firewood. Storage tanks are capable of accumulating excess thermal energy and smoothly releasing it into heating circuits.
Let's try to explain the principle of working on the fingers:
The simplicity of the thermal accumulator design not only increases the reliability of the unit, but also simplifies repairs and scheduled maintenance.
- Installed in a heating system with a heat accumulator, the heating boiler is loaded with firewood and produces a large amount of thermal energy;
- The resulting energy is sent to a thermal battery and accumulates there;
- At the same time, with the help of a heat exchanger, heat is collected for the heating system.
The buffer tank for heating (also known as a heat accumulator) operates in two modes - accumulation and release. In this case, the boiler power may exceed the required thermal power to heat the home. While the wood is burning in the firebox, heat will accumulate in the thermal accumulator. After the logs go out, energy will continue to be drawn from the battery for a long time.
Lazhebok’s heat accumulators for greenhouses and greenhouses are designed in approximately the same way - during the day they accumulate heat from the sun, and at night they release it, warming the plants and preventing them from freezing. They just look a little different.
Heat accumulators for heating systems are also necessary if solar panels or solar panels are used as a heat source. heat pumps. The same batteries cannot provide heat around the clock, since at night their efficiency drops to zero. During daylight hours, they will not only heat the house, but also accumulate thermal energy in a storage tank.
Heat accumulators can be useful when using electric boilers . This scheme justifies itself on a two-tariff payment system. In this case, the system is configured so that heat accumulation occurs at night, and its release begins during the day. Thanks to this, consumers have the opportunity to save money on energy consumption.
Types of heat accumulators
The heat accumulator for the heating system is a capacious tank equipped with solid thermal insulation - it is responsible for minimizing heat loss. Using one pair of pipes, the battery is connected to the boiler, and using the other pair, to the heating system. Additional pipes may also be provided here to connect the DHW circuit or additional sources of thermal energy. Let's look at the main types of heat accumulators for heating systems:

With a circulation pump, it becomes possible to use several buffer tanks at once, which allows you to evenly heat several rooms at once.
- Buffer tank is a simple tank without internal heat exchangers. The design provides for the use of the same coolant in the boiler and batteries, at the same permissible pressure. If you plan to pass one coolant through the boiler and another through the batteries, you should connect an external heat exchanger to the heat accumulator;
- Thermal accumulators for individual heating with lower, upper or several heat exchangers at once - such heat accumulators allow you to organize two independent circuit. The first circuit is a tank connected to the boiler, and the second is a heating circuit with batteries or convectors. The coolants do not mix here; there may be different pressures in both circuits. Heating is carried out using a heat exchanger;
- With a flow-through heat exchanger of the DHW circuit or with a tank - for organizing hot water supply. In the first case, water can be consumed throughout the day and evenly. The second scheme involves the accumulation of water for the purpose of its rapid release at a certain time (for example, in the evening, when everyone takes a shower before going to bed) - indirect boilers that accumulate water are designed in a similar way.
The design of heat accumulators for heating can be very different; the choice of a suitable option depends on the complexity of the heating system, its characteristics and the number of sources of hot coolant.
Some heat accumulators are equipped with heating elements with thermostats, which makes it possible to provide consumers with heat at night, when the coolant has already cooled down and there is no one to throw firewood into the firebox. They are also useful when using heat pumps and solar panels.
Calculation of heat accumulator volume
We have come close to the most difficult issue - calculating the required volume of the heat accumulator. To do this, we will use the following formula – m=W/(K*C*Δt). The letter W denotes the amount of excess heat, K is the efficiency of the boiler (we indicate decimal), C is the heat capacity of water (coolant), and Δt is the temperature difference, determined by subtracting the temperature of the coolant on the return pipe from the temperature on the supply pipe. For example, it can be 80 degrees at the outlet and 45 at the return - in total we get Δt=35.
First, let's calculate the amount of excess heat. Let's assume that for a house with an area of 100 sq. m. we need 10 kW of heat per hour. The burning time on one stack of firewood is 3 hours, and the boiler power is 25 kW. Consequently, in 3 hours the boiler will generate 75 kW of heat, of which only 30 kW needs to be sent for heating. In total, we are left with 45 kW of excess heat - this is enough for another 4.5 hours of heating. So as not to lose given heat and do not reduce the amount of loaded firewood (otherwise we will simply overheat the system), you should use a heat accumulator.
As for the heat capacity of water, it is 1.164 W*hour/kg*°C - if you don’t understand physics, just don’t go into details. And remember that if you use a different coolant, its heat capacity will be different.

Having carried out the necessary calculations using our advice, you can easily select the model that most accurately satisfies all your needs.
In total, we have all four values - this is 45,000 W of heat, the efficiency of the boiler (let's assume 85%, which in fractional calculations will be 0.85), the heat capacity of water is 1.164 and the temperature difference is 35 degrees. We carry out calculations - m=45000/(0.85*1.164*35). With these figures, the volume is equal to 1299.4 liters. We round up and get the capacity of the heat accumulator for our heating system equal to 1300 liters.
If you cannot carry out the calculations yourself, use special calculators, auxiliary tables or the help of specialists.
Connection diagrams
The simplest diagram for connecting a heat accumulator to solid fuel boiler involves the use of the same coolant at equal pressure in the boiler and heating system. For these purposes, the simplest storage tank without heat exchangers is suitable. Two pumps are installed on the return pipes - by adjusting their performance, we will ensure temperature control in the heating system. There is a similar scheme using a three-way valve - it allows you to regulate the temperature by mixing the hot coolant and the cooled coolant from the return pipe.
Heat accumulators with a built-in heat exchanger are designed to work in heating systems with high pressure coolant. To do this, heat exchangers are located inside them, connected through a circulation pump to the boilers - this is how a supply circuit is formed. Internal storage capacity with second circulation pump and batteries forms a heating circuit. Different coolants can circulate in both circuits, for example, water and glycol.
The design of a solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator and a hot water circuit allows for the supply of hot water without the use of dual-circuit equipment. For this purpose, internal flow-through heat exchangers or built-in tanks are used. If hot water is needed throughout the day, we recommend purchasing and installing a heat accumulator with a flow exchanger. For peak one-time consumption, batteries with hot water tanks are optimal.
Bivalent and multivalent connection schemes have also been developed - they involve the use of several heat sources at once for heating operation. For this purpose, heat accumulators with several heat exchangers can be used.
Popular models
It's time to understand the most popular models of heat accumulators for heating systems. We will consider products from domestic and foreign manufacturers.

The manufacturer of Prometheus heat accumulators is the Novosibirsk company SibEnergoTerm. It produces models with volumes of 230, 300, 500, 750 and 1000 liters. The equipment warranty is 5 years. The heat accumulators are equipped with four outlets for connection to heating and heat sources. A layer of thermal insulation made of mineral wool is responsible for preserving the accumulated energy. The working pressure is 2 atm, the maximum is 6 atm. When purchasing equipment, take into account its dimensions - for example, the diameter of a 1000-liter model is 900 mm, which is why its body may not fit into standard doorways 80 cm wide.
The price of the presented heat accumulator for heating systems varies in the range from 65 to 70 thousand rubles.

Another capacious heat accumulator for 1000 liters of water. It is equipped with one or two smooth-tube heat exchangers, but lacks thermal insulation, which must be taken into account when installing it - it will have to be purchased separately. The diameter of the case is 790 mm, but if thermal insulation is added to it, the diameter increases to 990 mm. The maximum temperature in the heating system is +110 degrees, in the DHW circuit – up to +95 degrees.

These heat accumulators are available in modifications with six or ten connections. There are also terminals on board temperature sensors. The tank capacity is 960 liters, operating pressure– up to 3 bar. The thickness of the thermal insulation layer is 80 mm. The use of liquids other than water as a coolant is not allowed - this applies to both circuits, and not just the heating circuit. If necessary, it is possible to connect several heat accumulators in series into a single cascade.
Homemade heat accumulators
Nothing prevents you from assembling a heat accumulator for a heating system with your own hands - for this you need to carry out calculations and draw a drawing, focusing on the required capacity. Tanks are constructed from sheet metal 1-2 mm thick, cut with a plasma cutter, cutting machine or welding machine. Heat exchangers are organized from metal straight or corrugated pipes. And in order to avoid rapid corrosion of the metal, you need to purchase a magnesium anode. Basalt wool can be used as thermal insulation.

As a bonus, we provide a detailed drawing of a heat accumulator with a capacity of 500 liters - this is enough to maintain the operation of the heating system in a small house.
Video
Heat accumulator for heating boilers
We continue our series of articles with a topic that will be of interest to those who heat their homes with solid fuel boilers. We will tell you about a heat accumulator for heating boilers (HS) using solid fuel. This is a really necessary device that allows you to balance the operation of the circuit, smooth out temperature changes in the coolant, and also save money. Let us immediately note that a heat accumulator for electric heating boilers is used only if the house has an electric meter with separate calculation of night and day energy. Otherwise, installing a heat accumulator for gas heating boilers makes no sense.
How does a heating system with a heat accumulator work?
A heat accumulator for heating boilers is a part of the heating system designed to increase the time between loading solid fuel into the boiler. It is a reservoir into which there is no air access. It is insulated and has a fairly large volume. There is always water in the heat accumulator for heating, and it circulates throughout the entire circuit. Of course, non-freezing liquid can also be used as a coolant, but still, due to its high cost, it is not used in circuits with TA.
In addition, there is no point in filling a heating system with a heat accumulator with antifreeze, since such tanks are placed in residential premises. And the essence of their use is to ensure that the temperature in the circuit is always stable, and therefore the water in the system is warm. The use of a large heat accumulator for heating in temporary country houses is impractical, and a small reservoir is of little use. This is due to the operating principle of the heat accumulator for the heating system.
- TA is located between the boiler and the heating system. When the boiler heats the coolant, it enters the heat exchanger;
- then the water flows through pipes to the radiators;
- the return flow returns to the TA, and then directly to the boiler.
Although the heat accumulator for the heating system is a single vessel, due to its large size, the direction of the flows at the top and bottom are different.
In order for the TA to perform its main function of storing heat, these flows must be mixed. The difficulty is that high temperatures always rise, and cold tends to fall. It is necessary to create such conditions so that part of the heat sinks to the bottom of the heat accumulator in the heating system and heats the return coolant. If the temperature is equalized throughout the tank, then it is considered fully charged.
After the boiler has burned out everything that was loaded into it, it stops working and the TA comes into play. The circulation continues and it gradually releases its heat through the radiators into the room. All this happens until the next portion of fuel enters the boiler again.
If the heat accumulator for heating is small, then its reserve will last only for a short time, while the heating time of the batteries increases, since the volume of coolant in the circuit has become larger. Disadvantages of using for temporary residences:
- the room warm-up time increases;
- larger volume of the circuit, which makes filling it with antifreeze more expensive;
- higher installation costs.
As you understand, filling the system and draining water every time you come to your dacha is troublesome, to say the least. Considering that the tank alone will be 300 liters, it makes no sense to take such measures for the sake of a few days a week.
Built into the tank additional circuits- These are metal spiral pipes. The liquid in a spiral does not have direct contact with the coolant in the heat accumulator for heating the house. These could be contours:
- low temperature heating (warm floor).
Thus, even the most primitive single-circuit boiler or even stove can become a universal heater. It will provide the entire house with the necessary heat and hot water at the same time. Accordingly, the heater's performance will be fully used.
In serial models manufactured in production conditions, built-in additional sources heating These are also spirals, only they are called electric heating elements. There are often several of them and they can work from different sources:
- circuit;
- solar panels.
This heating refers to additional options and is not mandatory, keep this in mind if you decide to make a heat accumulator for heating with your own hands.
Heat accumulator wiring diagrams
We dare to suggest that if you are interested in this article, then, most likely, you have decided to make a heat accumulator for heating and its wiring with your own hands. You can come up with many connection schemes, the main thing is that everything works. If you correctly understand the processes occurring in the circuit, then you can experiment. How you connect the TA to the boiler will affect the operation of the entire system. Let's first look at the simplest heating scheme with a heat accumulator.
A simple TA strapping scheme
In the figure you see the direction of movement of the coolant. Please note that upward movement is prohibited. To prevent this from happening, the pump between the heating element and the boiler must pump a larger amount of coolant than the one that stands before the tank. Only in this case will a sufficient drawing force be generated, which will remove part of the heat from the supply. The disadvantage of this connection scheme is the long heating time of the circuit. To reduce it, you need to create a boiler heating ring. You can see it in the following diagram.

Scheme of piping TA with boiler heating circuit
The essence of the heating circuit is that the thermostat does not add water from the heater until the boiler warms it up to the set level. When the boiler has warmed up, part of the supply goes into the TA, and part is mixed with coolant from the reservoir and enters the boiler. Thus, the heater always works with an already heated liquid, which increases its efficiency and the heating time of the circuit. That is, the batteries will become warm faster.
This method of installing a heat accumulator in a heating system allows you to use the circuit in autonomous mode when the pump will not work. Please note that the diagram shows only the connection points of the heating unit to the boiler. The coolant circulates to the radiators in a different way, which also passes through the heat exchanger. The presence of two bypasses allows you to be on the safe side twice:
- the check valve is activated if the pump is stopped and the ball valve on the lower bypass is closed;
- in case of pump stop and breakdown check valve circulation is carried out through the lower bypass.
In principle, some simplifications can be made to this design. Given the fact that the check valve has high flow resistance, it can be excluded from the circuit.

TA piping diagram without a check valve for a gravity system
In this case, when the light goes out, you will need to manually open the ball valve. It should be said that with such a layout, the TA must be located above the level of the radiators. If you do not plan for the system to operate by gravity, then connecting the heating system to the heat accumulator can be done according to the diagram shown below.
TA piping diagram for a circuit with forced circulation
The correct movement of water is created in the TA, which allows it to be heated ball by ball, starting from the top. The question may arise, what to do if there is no light? We talked about this in the article about sources alternative nutrition for the heating system. It will be more economical and convenient. After all, gravity contours are made of large-section pipes, and in addition, inclines that are not always convenient must be observed. If you calculate the price of pipes and fittings, weigh all the inconveniences of installation and compare all this with the price of a UPS, then the idea of installing alternative source nutrition will become very attractive.
Calculation of heat storage volume

Heat accumulator volume for heating
As we have already mentioned, it is not advisable to use small-volume TAs, and tanks that are too large are also not always appropriate. So the question has arisen about how to calculate required volume TA. I really want to give a specific answer, but, unfortunately, there cannot be one. Although there is still an approximate calculation of a heat accumulator for heating. Let's say you don't know what heat loss your house has and you can't find out, for example, if it hasn't been built yet. By the way, to reduce heat loss, you need to insulate the walls of a private house under the siding. You can select a tank based on two values:
- area of the heated room;
- boiler power.
Methods for calculating the volume of heating equipment: room area x 4 or boiler power x 25.
It is these two characteristics that are decisive. Different sources offer their own method of calculation, but in fact these two methods are closely interrelated. Suppose we decide to calculate the volume of a heat accumulator for heating, based on the area of the room. To do this, you need to multiply the square footage of the heated room by four. For example, if we have little house 100 sq. m., then you will need a tank of 400 liters. This volume will allow reducing the boiler load to twice a day.
Undoubtedly, this is true pyrolysis boilers, in which fuel is added twice a day, only in this case the operating principle is slightly different:
- the fuel flares up;
- air supply decreases;
- the smoldering process begins.
In this case, when the fuel flares up, the temperature in the circuit begins to increase rapidly, and then smoldering keeps the water warm. During this very smoldering, a lot of energy disappears into the pipe. In addition, if a solid fuel boiler works in tandem with a leaky heating system, then at peak temperatures the expansion tank sometimes boils. Water literally begins to boil in it. If the pipes are made of polymers, then this is simply destructive for them.
In one of the articles about polymer pipes we talked about their characteristics. The TA takes away some of the heat and the tank can boil only after the tank is fully charged. That is, the possibility of boiling, with the correct volume of TA, tends to zero.
Now let's try to calculate the volume of the heater based on the number of kilowatts in the heater. By the way, this indicator is calculated based on the square footage of the room. At 10 m 1 kW is taken. It turns out that in a house of 100 square meters there should be a boiler of at least 10 kilowatts. Since the calculation is always done with a margin, we can assume that in our case there will be a 15 kilowatt unit.
If you do not take into account the amount of coolant in the radiators and pipes, then one kilowatt of the boiler can heat approximately 25 liters of water in the heating unit. Therefore, the calculation will be appropriate: you need to multiply the boiler power by 25. As a result, we will get 375 liters. If we compare with the previous calculation, the results are very close. Only this takes into account that the boiler power will be calculated with a gap of at least 50%.
Remember, the more TA, the better. But in this matter, as in any other, one must do without fanaticism. If you install a TA for two thousand liters, then the heater simply cannot cope with such a volume. Be objective.
utepleniedoma.com
Thermal accumulator in the heating system
The heating system includes, in the usual concept that has developed over the years, three elements - a heat source (boiler), pipelines and directly heating devices(radiators). But if this a private house with a solid fuel boiler (wood, peat briquette, coal) and you want to increase efficiency and save yourself from the need to constantly monitor the firebox, then it may be worth using a unit such as a heat accumulator in the system. [content]
Operating principle of a heat accumulator
The main task performed by the heat accumulator is to increase the inertia of the heating system. To do this, they increase the volume of the coolant and, consequently, the amount of heat accumulated by it. Thus, the battery represents an insulated container embedded in the heating circuit.
As mentioned above, the battery significantly increases the inertia of the system, that is, although the coolant takes longer to heat up, it accumulates more heat and releases it longer and reduces temperature surges.

Internal structure of the heat accumulator
Thus, if the house is connected to central heating or the system uses gas or liquid fuel boilers operating in automatic mode as heat generating equipment, heat accumulators are simply extra costs material and means. But there are cases when their use is more than justified:
- If the heating system uses solid fuel boilers (especially without bunker loading), and it is not possible to ensure their constant maintenance (in a private house). In this case, the heat accumulator will provide a constant stable temperature in the room, and will even be able to smooth out the inevitable surges during cleaning and ash removal;
- If electric water heating is used and a differentiated system of payment for electricity is used. Heat accumulators will allow you to accumulate heat during hours when the tariff is minimal, and later on you can use heaters at minimum power;
- If the heating system has periods of peak heat energy consumption (most often this is due to the cost of heating water, for example, during intensive operation of showers), and installing an additional boiler is impractical. The battery will be able to provide heat transfer during these usually short periods of time.
Where the heat accumulator will be “superfluous”
Sometimes for heating systems the opposite is desirable speed dial temperature and its decrease, in this case, the increased amount of coolant that accumulates in the storage tanks will only interfere with rapid heating and cooling and precise temperature control. In particular:
- If heating is needed only for short periods of time and excess fuel consumption is undesirable. For example, a boiler room works to heat a dryer, which is used only periodically. In this case, it makes no sense to heat the empty room from which the material has been unloaded with accumulated heat.
- If, in addition to heating, the heating installation is also used to provide heat for some technological equipment and a quick and accurate change in temperature conditions is required - increased inertia will only get in the way.
How to install heat accumulators correctly
If a heating system with forced circulation is used, then the insertion point does not play much importance, since the delivery of thermal energy from the storage device is carried out by a pump. You can choose any convenient location, given that the battery has decent dimensions.
For its correct operation, it is necessary to correctly position the connecting pipes - the inlet (according to the movement of the thermal energy carrier in the system) at the bottom, the outlet at the top.

Heat accumulator connection diagram
If heating with natural circulation is used, then the insertion location plays a big role. Many people make the mistake of combining heat accumulators and expansion tanks. The expansion tank is located at the highest point of the heating and hot water from it can begin to move, only cooling down through the pipes and increasing its density. For efficient work The thermal energy accumulator should be located at the bottom of the heating supply pipe and as close as possible to the boiler.
Is it possible to assemble and install a thermal energy accumulator yourself?
From a design point of view, thermal energy accumulators are quite simple - they are a container with thermally insulated walls, equipped with pipes for connection to the heating system. Therefore, assembling or adapting containers for batteries will not be difficult for any person who has plumbing and welding skills.
The question may only arise of calculating the thermal insulation of the walls. But in this case, the principle “more is better than less” can be applied, since for tanks used as heat accumulators, due to their shape, there is no concept of an effective thermal insulation radius.
The video below shows the installation diagram and operating principle of the heat accumulator:
all-for-teplo.ru
Heat accumulator for heating system - main advantages. Press!
The desire of many owners of private houses and cottages to use resources to heat their homes as efficiently as possible quite often encounters the same problem - even when using all modern technologies insulation and energy saving, installation of the most economical heating boilers - there is no significant saving of resources.
This is largely a consequence of mistakes made long before the question of prudent use of resources and the use of modern construction technologies was raised. But what about new houses built according to all modern canons? Has the limit of development really reached?
For most, this will remain a rhetorical question, but for those who decide to use truly scientific knowledge, and not excerpts from advertising brochures, it is worth thinking about including a new element in the heating system - a heat accumulator.
How does the heating system work?
In the modern understanding of the energy efficiency of heating installations, including a separate house or cottage, the emphasis has recently shifted significantly from the indicator of fuel consumption for heating the room to an indicator characterizing the efficiency of energy use for the complete heating of the house.
This justified emphasis on energy efficiency allows us to take a fresh look at the problem of heating a home, which includes two main tasks:
- House heating;
- hot water supply.
A new way to save energy resources in the heating system of a building today is to install additional equipment in the heating system, the function of which is to accumulate thermal energy and gradually consume it.
The use of a heat accumulator in the circuit of heating system devices, where the main source of energy is a solid fuel boiler, makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption by up to 50% during the heating season without additional costs. But this is in the future, but for now we should clearly consider the operating principle of this device.
The principle of operation of a system with a solid fuel boiler
The highest effect from connecting to the system will be applied specifically to solid fuel boilers.
The heat released during fuel combustion goes through a heat exchanger through a pipeline into registers or heating batteries, which are essentially the same heat exchangers, only they do not receive heat, but, on the contrary, give it away to surrounding objects, air, in general, the heating room.
As it cools down, the coolant - water in the batteries - falls down and again flows into the boiler heat exchanger circuit, where it heats up again. In such a scheme, there are at least two points associated with large, if not enormous, heat loss:
- direct direction of coolant movement from the boiler to the registers and rapid cooling of the coolant;
- a small volume of coolant inside the heating system, which does not allow maintaining a stable temperature;
- the need to constantly maintain a consistently high coolant temperature in the boiler circuit.
It is important to understand that this approach cannot be called anything other than wasteful. After all, when adding fuel first at a high combustion temperature in the rooms, the air will warm up quite quickly. But as soon as the combustion process stops, the heating of the room will end, and as a result, the temperature of the coolant will drop again and the air in the room will cool down.
Using a heat accumulator
 Unlike a standard heating system, a system equipped with a heat accumulator works slightly differently. In its most primitive form, immediately after the boiler, the tank is installed as a buffer device.
Unlike a standard heating system, a system equipped with a heat accumulator works slightly differently. In its most primitive form, immediately after the boiler, the tank is installed as a buffer device.
A tank with multilayer thermal insulation is installed between the boiler and the pipelines. The capacity of the tank, and it is calculated in such a way that the amount of coolant inside the tank is greater than in the heating system, contains coolant heated from the boiler.
Several heat exchangers for the heating system and for the hot water supply system are installed inside the tank. The internal volume of the battery, heated by the boiler, can maintain high temperature and gradually give it away for heating and water supply systems.
Considering that the smallest tank has a volume of 350 liters of water, it is easy to calculate that spending the same amount of fuel when using a heat accumulator will have a much greater effect than with a direct heating system.
But this is the most primitive type of thermal device. A standard heat accumulator, designed to actually work in the heat supply conditions of a separate house, may have:
The price of such batteries depends on many factors:
- tank manufacturing material;
- volume of the internal tank;
- the material from which the heat exchanger is made;
- manufacturer's company;
- a set of additional equipment;
Specialist's note: calculate correct work The entire heating system, starting from the boiler heat output and ending with the diameter of the steam pipes, can, in principle, be done independently, but it should be taken into account that the power of both the boiler and the installation itself must be designed to operate at the lowest possible temperatures in the region.
More detailed information on this issue today can be found on the pages of Internet sites, both in text form and by using the services of specialized online calculators, and of course in specialized companies involved in the development and installation of heat supply systems.
Everything is controlled electronically
Perhaps for many such a concept as “ smart House“has long since become part of the usual rhythm of life.
A house in which many of the functions of maintaining and managing systems are taken over by electronics cannot do without the participation of electronic components and the operation of a heating and water supply system with a heat accumulator.
To maintain a consistently comfortable temperature, it is not so much the constant burning of fuel in the boiler firebox that is necessary, but rather the stable maintenance of temperature in the heating system. And electronic control of the heat accumulator’s operation copes with this task quite well.
Control board features:
In addition, the electronic component can be perfectly used as a controller for the operation of both a solid fuel boiler and electric heating devices, and even as a solar collector system to obtain maximum benefits and save resources.
The economic effect of even including a heat accumulator in the heating supply scheme allows, as already mentioned, to reduce fuel costs during the heating season by up to 50%, and if we take into account the fact that the price of energy is constantly growing, then such an investment becomes not only profitable, but already mandatory for new buildings.
Watch the video in which the user explains in great detail the design of a solid fuel boiler coupled with a heat accumulator:
heat.guru
Heat accumulator in a heating system: introduction to the principle of operation, design and installation options
Why are heat accumulators needed in heating systems? How are they built? When installing a heating system with your own hands, how can you connect the heat accumulator to the common circuit? Let's try to figure it out.

The hero of our article is in the photo on the right.
First meeting
What is it - a storage tank for heating?
In the very simple design- high cylindrical or square section container with several pipes on different heights from the base. Volume - from 200 to 3000 liters (the most popular models are from 0.3 to 2 cubic meters).
The list of options and options is quite large:
- The number of pipes can vary from four to a couple of dozen. It all depends on the configuration of the heating system and the number of independent circuits.
- The heat accumulator of water heating can be thermally insulated. 5-10 centimeters of polyurethane foam will greatly reduce unnecessary heat loss if the tank is located outside the heated room.
Advice: even if the tank is located inside the house and, it would seem, its heat transfer helps the radiators perform their functions - thermal insulation will not hurt. The amount of heat emitted by a tank with a volume of 0.3-2 cubic meters is VERY large. Our plans do not include organizing a 24-hour sauna.
- The wall material can be either black steel or stainless steel. It is clear that in the second case the service life of the heat accumulator is longer, but its price is also higher. By the way, in a closed system, water quickly becomes chemically inert, and the corrosion process of black steel is greatly slowed down.
- The tank can be divided into communicating sections by several horizontal partitions. In this case, the stratification of water by temperature inside its volume will be more pronounced.
- The tank can have flanges for mounting tubular electric heaters. In fact, with sufficient power, the hydraulic accumulator for heating systems will turn into a full-fledged electric boiler.
- The heat storage tank can be equipped with a heat exchanger for preparing hot drinking water. Moreover, this can be a flow-through plate heat exchanger or a storage tank inside the main tank. Compared to the amount of heat accumulated by the tank, the cost of heating water will in any case be insignificant.
- At the bottom of the tank there can be an additional heat exchanger for connecting a solar collector. It is at the bottom - to ensure effective heat transfer from the collector to the storage tank even when its efficiency is low (for example, at dusk).

This is how the heat accumulator is used in a solar heating system.
Functions
It is easy to guess that heating heat accumulators are needed in order to accumulate thermal energy in reserve. But even without them, the heating seems to work, and not bad. In what cases is their use justified?
Solid fuel boiler
For solid fuel boilers (with or without a water circuit), the most effective operating mode is one in which the fuel burns with a minimum amount of residue (including not only ash, but also acids and tar) and maximum efficiency - full power. Power adjustment is usually carried out by limiting air access to the firebox - with clear consequences.
However, to utilize all the thermal power means a short time heat the radiators almost red-hot, and then let them cool. This mode is extremely ineffective, leads to accelerated wear of pipes and their connections and provides uncomfortable temperature regime in the house.
This is where a heating system with a heat accumulator comes to the rescue:
- The heat generated by the boiler at full power is utilized to heat water in the tank.
- After the fuel burns out, water continues to circulate between storage tank and radiators, taking heat away from it GRADUALLY.
As a bonus, we get much less frequent firing of the boiler, which will save us both effort and time.

The buffer tank will allow the solid fuel boiler to operate in optimal mode.
Electric boiler
What are the benefits of heat storage heating when electricity is used as a heat source? After all, all modern electric boilers can regulate power smoothly or stepwise and do not require frequent maintenance?
The key phrase is night tariff. The cost of a kilowatt-hour with a two-tariff meter can be VERY different nights, when energy systems are unloaded, and during the day, at peak consumption.
By varying tariffs, energy workers distribute electricity consumption more evenly; Well, this is to our advantage:
- At night, the programmable boiler turns on according to a timer and heats the hydraulic accumulator for heating to its maximum operating temperature of 90 degrees.
- Accumulated during the day thermal energy used for heating homes. The coolant flow for heating systems is dosed by adjusting the performance of the circulation pump.

A heat accumulator in combination with a two-tariff meter will help significantly save on heating.
Multi-circuit heating
Another very useful feature storage tank - the ability to simultaneously use it as a hydraulic arrow while accumulating energy. What is it and why is it needed?
Remember that there are usually more than four pipes on the body of a tall tank. Although it would seem that entry and exit are quite enough. At different levels, water can be taken from the storage tank from different temperatures; as a result, we can get, most typically, a high-temperature circuit with radiators and low-temperature heating - heated floors.
Please note: pumps with thermal control circuits will still be needed. IN different time day at the same tank level, the water temperature will vary greatly.
The pipes can be used not only as outlets for heating circuits. Several boilers different types can also be connected to a heat accumulator.
Connection and thermal capacity
What does a heating system with a heat accumulator look like?
Heat accumulators for heating are connected in exactly the same way as hydraulic arrows and, in general, differ from them only in thermal insulation and volume. They are placed between the supply and return pipelines leading from the boiler. The supply is connected to the top of the tank, the return to the bottom.
Secondary circuits are powered depending on the temperature of the coolant they require: high-temperature heating takes water from the upper part of the tank, low-temperature heating from the lower part.

Schematic diagram of connection.
Instructions for calculating thermal capacity are based on a simple formula: Q = mc(T2-T1), where:
- Q - accumulated heat;
- m is the mass of water in the tank;
- With - specific heat coolant in J/(kg*K), for water equal to 4200;
- T2 and T1 - initial and final temperatures of the coolant.
Let's say, a heat accumulator with a volume of two cubic meters at a temperature delta of 20C (90-70) and using water as a coolant can accumulate 2000 kg (let's take the density of water as 1 kg/l, although at 90C it is slightly less) x4200 J/(kg*K)x20= 168,000,000 Joules.
What does this amount of energy mean? The tank can deliver 168 megawatts of thermal power in one second or, more realistically, 5 kilowatts in 33,600 seconds (9.3 hours).
Conclusion
As usual, you can learn more about heat accumulators by watching the video attached to the article (see also the water heating diagram for a private house).
Corrugated pipe for heating
Good day everyone! If you have come to this page of my blog, then you are interested in at least 2 questions:
- What is a heat accumulator?
- How does a heat accumulator work?
I'll start answering these questions in order.
What is a heat accumulator?
To answer this question we need to give a definition. It sounds like this: a heat accumulator is a container in which a large volume of hot coolant accumulates. The outside of the container is covered with thermal insulation made of mineral wool or polyethylene foam.

Why do you need a heat accumulator?
You ask: “Why do we need this oversized thermos?” Everything is very simple here; it allows you to optimally use the heat given off by the boiler. A powerful boiler (most often) always works in conjunction with a heat accumulator. The boiler quickly and non-stop transfers heat from the burned fuel to the heat accumulator, and it, in turn, slowly and in the required mode transfers this heat to the heating system. The system volume is much smaller than the battery capacity. This allows you to “stretch” the heat from the fuel over time. It turns out essentially. When the battery capacity is heated, the boiler constantly operates at full power, and this avoids the appearance of tarry condensate in the boiler.
How does a heat accumulator work?
As mentioned above, TA is a container in which hot water (or other) accumulates. To make everything clear, look at the following figure: 

The container has several pipes for connecting various equipment:
- Thermal energy generator - boiler, .
- Plate heat exchanger for heating hot water.
- Various boiler equipment - safety group, expansion tank and so on.
Materials of water-containing container.
- Carbon steel various brands with (or without) protective enamel or varnish applied to inner surface- the cheapest and therefore most common material.
- Stainless steel is the most durable material, which is not subject to corrosion. Its main disadvantage is the high price.
- Fiberglass - this “exotic” material is used to make dismountable heat accumulators, which are assembled directly on site. This method allows you to carry the TA along the narrowest stairs and assemble it exactly in in the right place. If interested, watch the video of what it looks like
Heat accumulator connection diagram.
Now let's look at how the battery is included in the heating system:


From this diagram it can be seen that the TA is included in the heating system as a hydraulic separator (). I recommend reading a separate article dedicated to this useful device. Let me say briefly that this switching scheme eliminates the mutual influence of different ones and makes it possible to provide the boiler with the required volume of coolant, which has a positive effect on the life of the heat exchanger.
Thermal storage and hot water supply.
Another important issue is the installation of hot water supply in the house. This is where TA can also come to the rescue. Of course, you cannot use water directly from the heating system for sanitary needs. But there are at least two solutions here:
- Connecting a plate heat exchanger to the TA, in which sanitary water will be heated - used at the most simple models TA.
- Purchasing a heat accumulator with a built-in hot water system - it can be implemented either using a separate heat exchanger (coil) or according to the “tank in tank” scheme.


You can, of course, also purchase separately, but I believe that this can only be done if you have required space in your boiler room.
Summary.
A heat accumulator is another way to increase the time between adding fuel to the boiler. In addition, TA can be used in systems with solar collectors and heat pumps. Most often, TA is used as a replacement for long-burning boilers. The alternative is certainly interesting and worthy of your attention. This concludes my story. I look forward to your questions in the comments.






